-
Technology ConsultingTechnology Consulting
-
Custom Software DevelopmentCustom Software Development
-
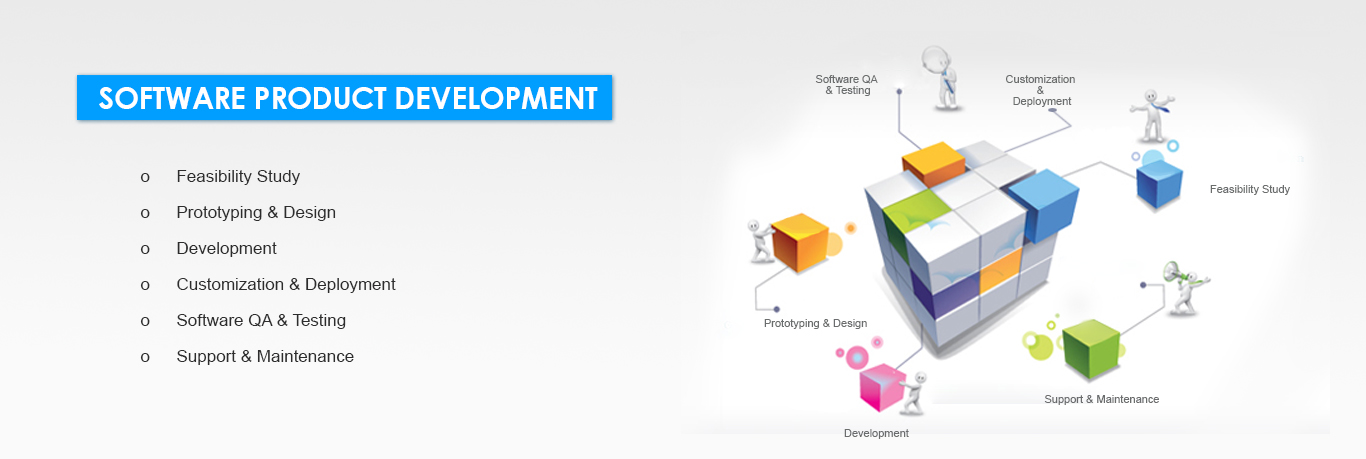
Software Product DevelopmentSoftware Product Development
-
Mobile OfferingsMobile Offerings
-
CMS(Content Management Solutions)&Ecommerce OfferingsCMS(Content Management Solutions)&Ecommerce Offerings
-
SEO & Internet MarketingSEO & Internet Marketing
-
Maintenance and SupportMaintenance and Support
-
Finance and AccountingFinance and Accounting
- Technology
- Tools & Techniques
- Why Acrossys
- Solutions
- Automate routine procedures (builds creation, regression testing and others)
- Application Integration & Customization
- Use requirements management tools
- Use video and audio-conferencing tools for regular communication between physically distributed teams
- Use issue (defect, CR, etc) tracking systems
- Use SCM tool with multi-branching support
- Use Helpdesk and Knowledge Base systems
Product Leadership
We identify Business Analysis in Software Product Development as a separate area of expertise, targeted to extend capabilities and facilitate your central Product Management efforts. This helps your Product Manager to scale properly and focus on the most critical things, without being overloaded by a huge amount of information from users or multiple products requirements management tasks, etc..
Focus on Product Quality
All product quality assurance functions are handled by an independent QA department whose sole mission is the quality of your product at its every aspect. Independence from the development team guarantees that you always get correct understanding of the quality and will be able to make informed decisions based on that information.
Intellectual Property Protection
Acrossys has a strong focus on a service-based business model. This is one of the principal points we are building our work around and it is designed and implemented to protect Acrossys’s clients from unfair competition practices. Strong corporate policies, standards and infrastructure protect client Intellectual Property from being used by anybody else, including other product teams within Acrossys.
Feasibility Study
Requirements are statements that point towards what a system ought to perform in...

Prototyping & Design
Design phase can be divided into two...

Development:
The complete assessment and evaluation of a system is done once the design phase...
Customization & Deployment:
Upon development of the product, the entire code needs to be deployed in the rel...

Software QA & Testing
This phase involves testing of the code written in the coding phase to discern t...

Support & Maintenance
This process comes into picture once the software is installed at the customer’s...
- Feasibility Study
Requirements are statements that point towards what a system ought to perform in order to provide a capability (i.e. utility or benefit) which are generally prepared during the early stages of a project’s system development lifecycle (SDLC).
Requirements have to be defined with accuracy and this is critical to the success of a project since they describe what the users want a system to perform. Bad requirements are direct attributes to a majority of the software defects. Fixation of an error during the implementation stage is of larger magnitude than doing the same during the analysis stage. Based on the level of details provided, different names are used to requirements documentation like business requirements, user requirements, functional requirements etc.

- Prototyping & Design
Prototyping and Design Phase
Design phase can be divided into two:
High level design : The complete System Design is given in a High Level Design (HLD) and this includes Functional Architecture and Database Design. All the modules, from the main module to all sub modules are designed in this stage. The flow of the system is hence well understood by the developers. The Review team, i.e. the testers and the end users (customers) play a vital role. The entry criteria for this is the requirement document, commonly known as the SRS (Software Requirement Specifications). And HLD, projects standards, the functional design documents, and the database design document forms the exit criteria. In short, High Level Design describes how the program is to be broken down into various modules.
Low level design : In the detailed phase, while defining the Low Level Design, the application obtained after the high level design is further broken down into modules and programs. A unit test plan is created for every program. The HLD document created in the previous phase forms the entry criteria for this stage. And the program specification and LLD (unit test plan) will be the exit criteria. If the analysis made is proper and an accurate and precise Low Level Design document is drafted, it makes the developers’ job painless, since the code can be developed directly from LLD. This keeps the debugging and testing efforts also nominal.
- Development
Development:
The complete assessment and evaluation of a system is done once the design phase is completed. The next phase – coding phase, aims at translating the design created into a set of programs in some given programming language, so that the design can be implemented in the most efficient manner. This phase affects the subsequent phases, such as testing and maintenance, acutely. While coding, the focus has to be on minimizing testing and maintenance effort. All endeavors while coding should stand for simplicity and lucidity.

- Customization & Deployment
Upon development of the product, the entire code needs to be deployed in the relevant environment for further testing to ensure the product functions in the desired quality and without any breaks.

- Software QA & Testing
This phase involves testing of the code written in the coding phase to discern the result of the application developed. The detected defects, if any, are then to be raised. Test execution is the process where the software developed is tested on the basis of test documents. The errors are then reported to the development team.

- Support & Maintenance
Support & Maintenance:
This process comes into picture once the software is installed at the customer’s location. It includes all the activities performed to maintain the system up and running. The main two forms of maintenance activities are :
Adaptive maintenance:
When the system in question is large, elimination of all the faults before delivery is practically close to impossible. The correction of errors as and when they are found are the activities included in adaptive maintenance.
Corrective Maintenance:
When software is installed in a new environment, it often changes what is desired from the system. The close and direct interaction of the users with the software helps them to identify newer and more precise needs which couldn’t be captured during the requirement analysis. Changes are found in output formats and system environment too. This calls for modification of the software and the maintenance activities related to such changes comes under Corrective maintenance.
Maintenance involves the following:
– A good knowledge of the existing software
– Better comprehension of the outcome of the changes
– Putting the changes to action – both the documents and code
– Retesting the modified parts and resetting the old portions.